A comprehensive multi-agent system for automated competitor analysis, this isn't just another AI project - it's a production-ready system that demonstrates how to build reliable, scalable agentic workflows with proper validation, error handling, and quality assurance.
Why Multi-Agent Systems?
Traditional single-agent approaches often struggle with complex, multi-stage tasks that require different types of reasoning and expertise. A competitor analysis workflow, for example, needs:
- Planning: Breaking down high-level requests into actionable tasks
- Data Collection: Gathering information from multiple sources
- Analysis: Transforming raw data into business insights
- Synthesis: Creating comprehensive reports
- Quality Control: Ensuring outputs meet standards at each stage
A multi-agent architecture allows each agent to specialize in its domain while working together through a coordinated workflow. This separation of concerns leads to better results, easier debugging, and more maintainable systems.
System Architecture Overview
The system uses LangGraph to orchestrate six specialized agents through a stateful workflow:
The Agent Team
- Planner Agent: Breaks down user requests into structured execution plans
- Supervisor Agent: Controls workflow flow, validates outputs, and applies business rules
- Data Collector Agent: Performs web searches and scrapes competitor information
- Insight Agent: Transforms raw data into SWOT analysis and business insights
- Report Agent: Generates comprehensive, formatted reports
- Export Agent: Creates professional PDF exports with customizable branding
Workflow Orchestration
The workflow follows a carefully designed state machine pattern that orchestrates all agents through a coordinated sequence with validation gates and intelligent retry mechanisms:
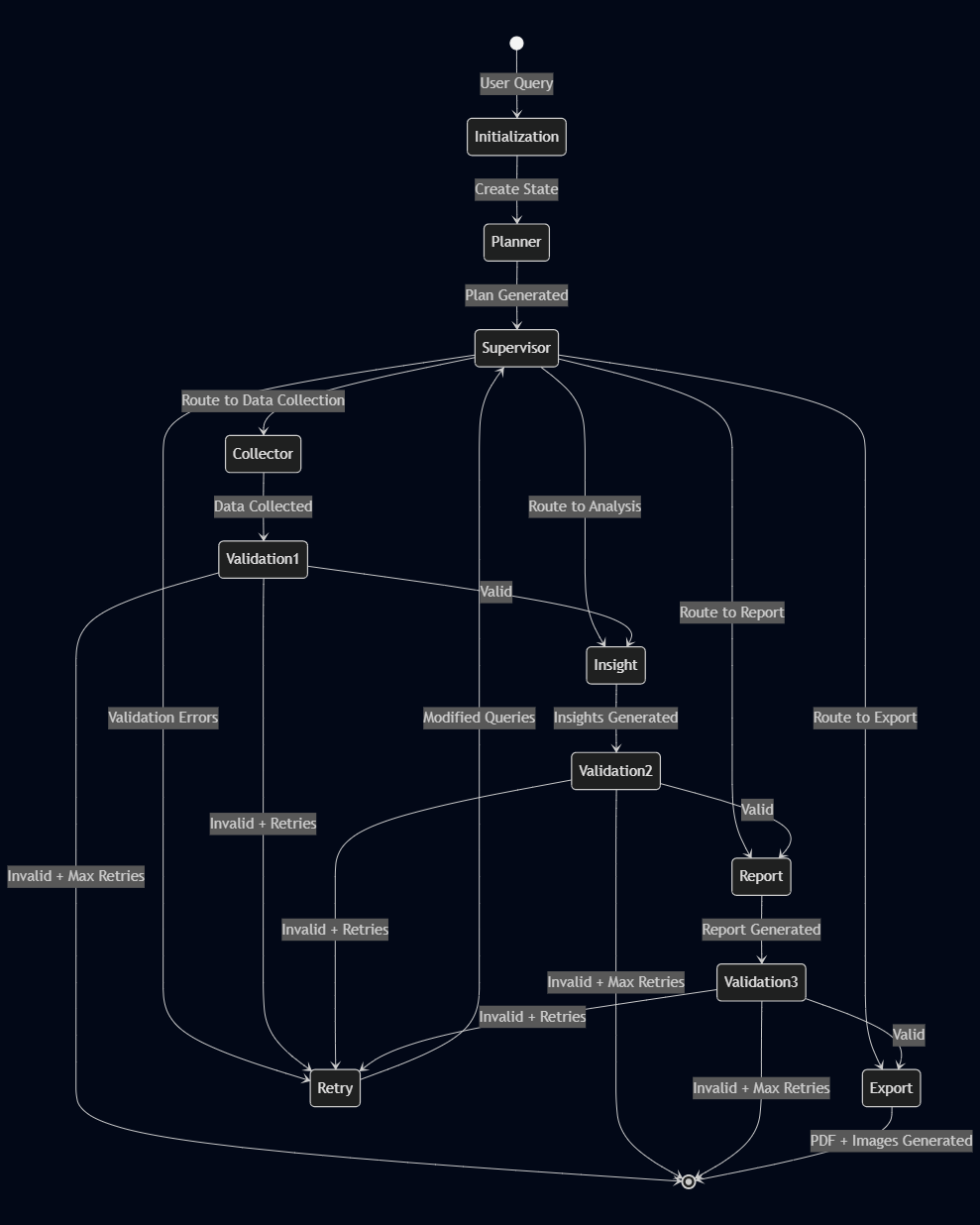
The diagram illustrates the complete flow from user query through initialization, planning, data collection, analysis, report generation, and export. Each stage includes validation gates that ensure quality before proceeding. If validation fails, the system intelligently retries with improved queries, analyzing the validation errors to understand what went wrong and how to fix it. The workflow gracefully handles errors and can terminate if maximum retries are exceeded.
Key Architectural Decisions
1. Immutable State Management
State updates follow immutability principles to prevent accidental mutations. Instead of modifying existing state objects, the system creates new state objects with the updated values. This ensures that state transitions are predictable and testable, and prevents bugs from shared state mutations.
2. Validation Gates at Each Stage
Quality control happens at every workflow stage, not just at the end:
- Collector Validator: Ensures minimum data requirements (sources, completeness)
- Insight Validator: Validates SWOT analysis quality and insight depth
- Report Validator: Checks report completeness and formatting
Validators return structured ValidationResult objects rather than raising exceptions, allowing the workflow to make intelligent decisions about retries and error handling.
3. Intelligent Retry Mechanism
When validation fails, the system doesn't just retry blindly. Instead, it uses an LLM to analyze the validation errors and improve the query automatically. The system examines what went wrong, understands the context of the failure, and generates an improved query that addresses the specific issues. This intelligent retry mechanism significantly improves success rates compared to simple retry loops.
4. Tiered Model Configuration
Different agents use different models based on task complexity. Planning and coordination agents use faster, lighter models optimized for speed, while analysis and report generation agents use more powerful models optimized for quality. This tiered approach optimizes both cost and performance, using expensive models only where they add value.
5. Comprehensive Error Handling
The system implements a custom exception hierarchy that categorizes different types of errors. This allows for precise error handling and better debugging. Each error type can be handled appropriately in the workflow, ensuring that failures are caught early and handled gracefully.
Performance Optimizations
LLM Response Caching
Frequently repeated queries are cached to reduce API costs. The system maintains an in-memory cache with a configurable size limit, using a least-recently-used eviction strategy when the cache is full. Caching is particularly effective for validation queries and common data collection patterns, significantly reducing redundant API calls.
Rate Limiting with Exponential Backoff
All LLM API calls are wrapped with automatic retry logic that uses exponential backoff. When rate limits are encountered, the system automatically waits with increasing delays before retrying, up to a maximum number of attempts. This ensures the system gracefully handles API rate limits and transient failures without manual intervention.
Async Support for I/O Operations
For operations that can run in parallel, the system supports async execution. Multiple data collection operations can be executed concurrently, significantly improving performance when gathering information from multiple sources simultaneously.
Quality Assurance Features
Agent Output Logging
Each agent's output is automatically logged to timestamped files in a dedicated logging directory. Each agent creates its own log file with a timestamp, making it easy to track what each agent produced at each stage of the workflow. This makes debugging and analysis much easier, you can see exactly what each agent produced at each stage.
Metrics and Monitoring
The system tracks detailed performance metrics:
- Execution time for each node and agent
- Token usage from LLM calls
- API call counts and success rates
- Validation pass/fail rates
Metrics are automatically exported to JSON files after workflow completion, enabling performance analysis and optimization.
LangSmith Observability
Optional integration with LangSmith provides comprehensive tracing:
- All LLM calls (requests, responses, tokens, latency)
- Agent operations and state transitions
- Workflow execution flow
- Error traces and retry attempts
This observability is invaluable for debugging complex workflows and understanding system behavior.
PDF Export System
The export system generates professional PDFs with extensive customization options:
Custom Branding
- Company logos and colors
- Custom fonts and typography
- Branded headers and footers
Multiple Cover Page Templates
- Default: Standard professional layout
- Executive: Minimal, executive-focused design
- Minimal: Clean, simple layout
Advanced Features
- PDF metadata (title, author, keywords)
- Automatic bookmarks and table of contents
- Flexible page layouts (size, orientation, margins)
- Markdown-to-PDF conversion with proper formatting
The PDF generation system uses a template engine that supports markdown, allowing for rich formatting while maintaining simplicity.
Testing and Quality Standards
The project maintains high quality standards:
- 80%+ test coverage: Comprehensive unit and integration tests
- Type safety: Full type hints throughout the codebase
- Code quality: Automated linting and static analysis tools
- Documentation: Comprehensive docstrings for all public APIs
- Parallel test execution: Fast test runs with parallel execution support
Test Architecture
Tests are organized into:
- Unit tests: Test individual components in isolation
- Integration tests: Test complete workflow execution
- Fixtures: Reusable test data and mocks
Parallel test execution significantly reduces test time, making the development feedback loop much faster.
Lessons Learned
Building this system taught me several valuable lessons:
1. Validation is Critical
Early validation prevents cascading failures. By validating at each stage, we catch issues immediately rather than discovering them at the end of a long workflow.
2. Retry Logic Needs Intelligence
Simple retry loops aren't enough. Using LLMs to analyze errors and improve queries dramatically increases success rates.
3. State Management Matters
Immutable state updates prevent entire classes of bugs. The discipline of creating new state objects rather than mutating existing ones pays off in maintainability.
4. Observability is Essential
Without proper logging and tracing, debugging multi-agent systems is nearly impossible. The investment in observability tools pays dividends.
5. Model Selection Affects Cost and Quality
Using the right model for each task optimizes both cost and quality. Not every agent needs the most powerful model.
Real-World Applications
This system architecture is applicable to many domains beyond competitor analysis:
- Market Research: Automated market analysis and trend identification
- Investment Research: Company and industry analysis
- Content Research: Automated research for content creation
- Business Intelligence: Automated report generation from multiple sources
- Due Diligence: Automated information gathering and analysis
The key is identifying workflows that benefit from multi-stage processing with different types of reasoning at each stage.
Future Enhancements
There's always room for improvement:
- Multi-language support: Analyze competitors in different languages
- Real-time data sources: Integration with live APIs and databases
- Advanced analytics: Statistical analysis and trend prediction
- Collaborative workflows: Multiple users contributing to analysis
- Custom agent types: Domain-specific agents for different industries
Conclusion
Building a production-ready multi-agent system requires careful attention to:
- Architecture: Proper separation of concerns and state management
- Quality: Validation gates and error handling at every stage
- Performance: Caching, rate limiting, and async operations
- Observability: Comprehensive logging and tracing
- Testing: High test coverage and parallel execution
The result is a system that's not just functional, but reliable, maintainable, and scalable. The multi-agent architecture provides flexibility and specialization that single-agent systems can't match, while the validation and retry mechanisms ensure quality and reliability.
If you're building agentic systems, I highly recommend:
- Start with a clear workflow design
- Implement validation gates early
- Invest in observability from the beginning
- Use appropriate models for each task
- Test thoroughly and maintain high coverage
The complete source code and documentation are available on GitHub. Feel free to explore, contribute, or use it as a reference for your own multi-agent projects!
Tech Stack: Python • LangGraph • LangChain • Groq • Tavily • ReportLab • Pydantic
Key Takeaway: Multi-agent systems excel when tasks require different types of reasoning at different stages. The key to success is proper orchestration, validation, and observability.




